Cardiopulmonary Bypass on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
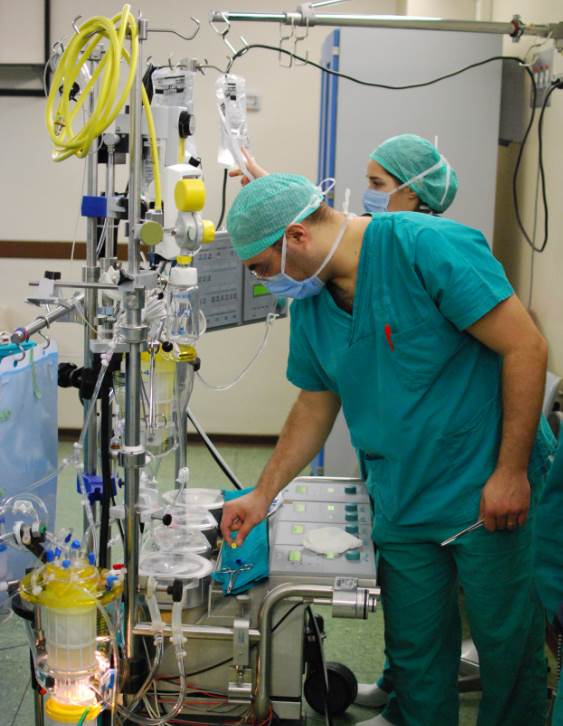
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the
 Cardiopulmonary bypass is commonly used in operations involving the heart. The technique allows the surgical team to oxygenate and circulate the patient's blood, thus allowing the surgeon to operate on the heart. In many operations, such as
Cardiopulmonary bypass is commonly used in operations involving the heart. The technique allows the surgical team to oxygenate and circulate the patient's blood, thus allowing the surgeon to operate on the heart. In many operations, such as
 The Austrian-German physiologist Maximilian von Frey constructed an early prototype of a heart-lung machine in 1885 at
The Austrian-German physiologist Maximilian von Frey constructed an early prototype of a heart-lung machine in 1885 at  The oxygenator was first conceptualized in the 17th century by
The oxygenator was first conceptualized in the 17th century by 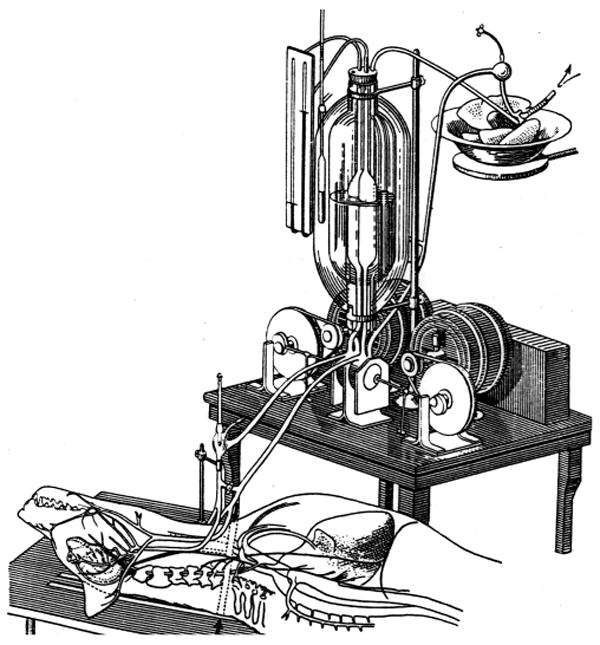 In 1983, Ken Litzie patented a closed emergency heart bypass system which reduced circuit and component complexity. This device improved patient survival after cardiac arrest because it could be rapidly deployed in non-surgical settings.
In 1983, Ken Litzie patented a closed emergency heart bypass system which reduced circuit and component complexity. This device improved patient survival after cardiac arrest because it could be rapidly deployed in non-surgical settings.
International Consortium For Evidence-Based PerfusionCircuitSurfers: A Perfusion Blog about Cardiopulmonary Bypass
*
Multimedia Manual of Cardiothoracic Surgery. Cardiopulmonary bypass collection.Profiles in Science: The Clarence Dennis Papers
Selected papers of Clarence Dennis, credited with the first attempt at cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. {{Authority control Medical equipment American inventions German inventions Soviet inventions
heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
and lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s during surgery
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pat ...
, maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen to the body. The CPB pump itself is often referred to as a heart–lung machine or "the pump". Cardiopulmonary bypass pumps are operated by perfusionist
A cardiovascular perfusionist, clinical perfusionist or perfusiologist, and occasionally a cardiopulmonary bypass doctor or clinical perfusion scientist, is a healthcare professional who operates the cardiopulmonary bypass machine (heart–lung ma ...
s. CPB is a form of extracorporeal
An extracorporeal is a medical procedure which is performed outside the body. Extracorporeal devices are the artificial organs that remain outside the body while treating a patient. Extracorporeal devices are useful in hemodialysis and cardiac surg ...
circulation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), also known as extracorporeal life support (ECLS), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequat ...
is generally used for longer-term treatment.
CPB mechanically circulates and oxygenates blood for the body while bypassing the heart and lungs. It uses a heart–lung machine to maintain perfusion to other body organs and tissues while the surgeon works in a bloodless surgical field. The surgeon places a cannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; plural or ) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces ...
in the right atrium, vena cava, or femoral vein to withdraw blood from the body. Venous blood is removed from the body by the cannula and then filtered, cooled or warmed, and oxygenated before it is returned to the body by a mechanical pump. The cannula used to return oxygenated blood is usually inserted in the ascending aorta, but it may be inserted in the femoral artery, axillary artery, or brachiocephalic artery (among others).
The patient is administered heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
to prevent clotting, and protamine sulfate
Protamine sulfate is a medication that is used to reverse the effects of heparin. It is specifically used in heparin overdose, in low molecular weight heparin overdose, and to reverse the effects of heparin during delivery and heart surgery. ...
is given after to reverse effects of heparin. During the procedure, hypothermia may be maintained; body temperature is usually kept at 28 °C to 32 °C (82.4–89.6 °F). The blood is cooled during CPB and returned to the body. The cooled blood slows the body's basal metabolic rate, decreasing its demand for oxygen. Cooled blood usually has a higher viscosity, but the crystalloid solution used to prime the bypass tubing dilutes the blood.
Uses
 Cardiopulmonary bypass is commonly used in operations involving the heart. The technique allows the surgical team to oxygenate and circulate the patient's blood, thus allowing the surgeon to operate on the heart. In many operations, such as
Cardiopulmonary bypass is commonly used in operations involving the heart. The technique allows the surgical team to oxygenate and circulate the patient's blood, thus allowing the surgeon to operate on the heart. In many operations, such as coronary artery bypass grafting
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft (CABG, pronounced "cabbage") is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest p ...
(CABG), the heart is arrested (i.e., stopped) because of the difficulty of operating on the beating heart. Operations requiring the opening of the chambers of the heart, for example, mitral valve repair
Mitral valve repair is a cardiac surgery procedure performed by cardiac surgeons to treat stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leakage) of the mitral valve. The mitral valve is the "inflow valve" for the left side of the heart. Blood flows fro ...
or replacement, requires the use of CPB to avoid engulfing air systemically and to provide a bloodless field to increase visibility for the surgeon. The machine pumps the blood and, using an oxygenator, allows red blood cells to pick up oxygen, as well as allowing carbon dioxide levels to decrease. This mimics the function of the heart and the lungs, respectively.
CPB can be used for the induction of total body hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe h ...
, a state in which the body can be maintained for up to 45 minutes without perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is deliver ...
(blood flow). If blood flow is stopped at normal body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
, permanent brain damage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating t ...
normally occurs in three to four minutes – death may follow shortly afterward. Similarly, CPB can be used to rewarm individuals who have hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe h ...
. This rewarming method of using CPB is successful if the core temperature of the patient is above 16 °C.
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), also known as extracorporeal life support (ECLS), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequat ...
) is a simplified version of the heart lung machine
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and oxygen to the body. The CPB pump itself is often referred to as a he ...
that includes a centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic ...
and an oxygenator to temporarily take over the function of heart and/or the lungs. ECMO is useful in post cardiac surgery patients with cardiac or pulmonary dysfunction, in patients with acute pulmonary failure, massive pulmonary embolisms
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
, lung trauma from infections, and a range of other problems that impair cardiac or pulmonary function. ECMO gives the heart and/or lungs time to repair or recover but is only a temporary solution. Patients with terminal conditions, cancer, severe nervous system damage, uncontrolled sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
and other conditions may not be candidates for ECMO.
Surgical procedures in which cardiopulmonary bypass is used
*Coronary artery bypass surgery
Coronary artery bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass graft (CABG, pronounced "cabbage") is a surgical procedure to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), the buildup of plaques in the arteries of the heart. It can relieve chest pai ...
*Cardiac valve repair and/or replacement (aortic valve
The aortic valve is a valve in the heart of humans and most other animals, located between the left ventricle and the aorta. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar valves, the other being the pulmonary valve. The ...
, mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-w ...
, tricuspid valve
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right vent ...
, pulmonic valve
The pulmonary valve (sometimes referred to as the pulmonic valve) is a valve of the heart that lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery and has three cusps. It is one of the four valves of the heart and one of the two semilunar v ...
)
*Repair of large septal
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate.
Examples
Human anatomy
* Interatr ...
defects (atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this d ...
, ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one ...
, atrioventricular septal defect
Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" (CAVC) or "endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the heart ...
)
*Repair and/or palliation of congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular ...
s (Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are:
*pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the ri ...
, transposition of the great vessels
Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenita ...
)
*Transplantation (heart transplantation
A heart transplant, or a cardiac transplant, is a surgical transplant procedure performed on patients with end-stage heart failure or severe coronary artery disease when other medical or surgical treatments have failed. , the most common procedu ...
, lung transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. ...
, heart–lung transplantation, liver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
)
*Repair of some large aneurysms
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus (s ...
(aortic aneurysm
An aortic aneurysm is an enlargement (dilatation) of the aorta to greater than 1.5 times normal size. They usually cause no symptoms except when ruptured. Occasionally, there may be abdominal, back, or leg pain. The prevalence of abdominal aortic ...
s, cerebral aneurysm
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a brain aneurysm, is a cerebrovascular disorder in which weakness in the wall of a cerebral artery or vein causes a localized dilation or ballooning of the blood vessel.
Aneurysms in the posterior circul ...
s)
*Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy
In thoracic surgery, a pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE), also referred to as pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA), is an operation that removes organized clotted blood (thrombus) from the pulmonary arteries, which supply blood to the lungs.
Indica ...
*Pulmonary thrombectomy
A pulmonary thrombectomy is an emergency surgical procedure used to remove blood clots from the pulmonary arteries.
Mechanical thrombectomies can be surgical (surgical thrombectomy) or percutaneous (percutaneous thrombectomy).
Surgical thrombect ...
*Isolated Limb perfusion
Contraindications and special considerations
There are no absolute contraindications to cardiopulmonary bypass. However, there are several factors that need to be considered by the care team when planning an operation.Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is the development of thrombocytopenia (a low platelet count), due to the administration of various forms of heparin, an anticoagulant. HIT predisposes to thrombosis (the abnormal formation of blood clots in ...
(HIT) and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and thrombosis (HITT) are potentially life-threatening conditions associated with the administration of heparin. In HIT or HITT, antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
against heparin are formed which causes platelet activation and the formation of blood clots
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cr ...
. Because heparin is typically used in CPB, patients who are known to have the antibodies responsible for HIT and HITT require alternative forms of anticoagulation. Bivalirudin
Bivalirudin (Bivalitroban), sold under the brand names Angiomax and Angiox and manufactured by The Medicines Company, is a direct thrombin inhibitor (DTI).
Chemically, it is a synthetic congener of the naturally occurring drug hirudin, found in ...
is the most studied heparin-alternative in patients with HIT or HITT requiring CPB.
A small percentage of patients, such as those with an antithrombin III deficiency
Antithrombin III deficiency (abbreviated ATIII deficiency) is a deficiency of antithrombin III. This deficiency may be inherited or acquired. It is a rare hereditary disorder that generally comes to light when a patient suffers recurrent venous ...
, may exhibit resistance to heparin. In these patients, patients may need additional heparin, fresh frozen plasma, or other blood products such as recombinant anti-thrombin III to achieve adequate anticoagulation.
A persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) is thoracic system variation in which the left-sided vena cava fails to involute during normal development. It is the most common variation of the thoracic venous system, occurring in approximately 0.3% of the population. The abnormality is often detected on pre-operative imaging studies, but may also be discovered intra-operatively. A PLSVC may make it difficult to achieve proper venous drainage or deliver of retrograde cardiopledgia. Management of a PLSVC during CPB depends on factors such as the size and drainage site of the PSLVC.
Risks and complications
CPB is not benign and there are a number of associated problems. As a consequence, CPB is only used during the several hours a cardiac surgery may take. CPB is known to activate the coagulation cascade and stimulate inflammatory mediators, leading to hemolysis and coagulopathies. This problem worsens as complement proteins build on the membrane oxygenators. For this reason, most oxygenators come with a manufacturer's recommendation that they are only used for a maximum of six hours, although they are sometimes used for up to ten hours, with care being taken to ensure they do not clot off and stop working. For longer periods than this, anECMO
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), also known as extracorporeal life support (ECLS), is an extracorporeal technique of providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequat ...
(extracorporeal membrane oxygenation) is used, which can be in operation for up to 31 days – such as in a Taiwanese case, for 16 days, after which the patient received a heart transplant.
The most common complication associated with CPB is a protamine
Protamines are small, arginine-rich, cell nucleus, nuclear proteins that replace histones late in the haploid phase of spermatogenesis and are believed essential for sperm head condensation and DNA stabilization. They may allow for denser packagin ...
reaction during anticoagulation reversal. There are three types of protamine reactions, and each may cause life-threatening hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dias ...
(type I), anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
(type II), or pulmonary hypertension (type III). Patients with prior exposure to protamine, such as those who have had a previous vasectomy
Vasectomy, or vasoligation, is an elective surgical procedure for male sterilization or permanent contraception. During the procedure, the male vasa deferentia are cut and tied or sealed so as to prevent sperm from entering into the urethra and ...
(protamine is contained in sperm) or diabetics
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased a ...
(protamine is contained in neutral protamine hagedorn (NPH) insulin formulations), are at an increased risk of type II protamine reactions due to cross-sensitivity. Because protamine is a fast-acting drug, it is typically given slowly to allow for monitoring of possible reactions. The first step in management of a protamine reaction is to immediately stop the protamine infusion. Corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involv ...
s are used for all types of protamine reactions. Chlorphenamine
Chlorphenamine (CP, CPM), also known as chlorpheniramine, is an antihistamine used to treat the symptoms of allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis (hay fever). It is taken by mouth. The medication takes effect within two hours and lasts ...
is used for type II (anaphylactic) reactions. For type III reactions, heparin is redosed and the patient may need to go back on bypass.
CPB may contribute to immediate cognitive decline. The heart-lung blood circulation system and the connection surgery itself release a variety of debris into the bloodstream, including bits of blood cells, tubing, and plaque. For example, when surgeons clamp and connect the aorta to tubing, resulting emboli may block blood flow and cause mini strokes. Other heart surgery factors related to mental damage may be events of hypoxia, high or low body temperature, abnormal blood pressure, irregular heart rhythms, and fever after surgery.
Components
Cardiopulmonary bypass consists of two main functional units, thepump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy. Pumps can be classified into three major groups according to the method they u ...
and the oxygenator
An oxygenator is a medical device that is capable of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood of human patient during surgical procedures that may necessitate the interruption or cessation of blood flow in the body, a critical organ or ...
which removes relatively oxygen-depleted blood from a patient's body and replaces it with oxygen-rich blood through a series of tubes (hoses). A heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contac ...
is used to control body temperature by heating or cooling the blood in the circuit. It is important that all components of the circuit are coated internally by heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
or another anticoagulant to prevent clotting within the circuit.

Tubing
The components of the CPB circuit are interconnected by a series of tubes made ofsilicone rubber Silicone rubber is an elastomer (rubber-like material) composed of silicone—itself a polymer—containing silicon together with carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Silicone rubbers are widely used in industry, and there are multiple formulations ...
or PVC.
Pumps
Centrifugal pump
Many CPB circuits now employ acentrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic ...
for the maintenance and control of blood flow during CPB. By altering the speed of revolution (RPM) of the pump head, blood flow is produced by centrifugal force
In Newtonian mechanics, the centrifugal force is an inertial force (also called a "fictitious" or "pseudo" force) that appears to act on all objects when viewed in a rotating frame of reference. It is directed away from an axis which is paralle ...
. This type of pumping action is considered to be superior to the action of the roller pump by many because it is thought to prevent overpressurization, clamping or kinking of lines, and produce less damage to blood products (hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo o ...
, etc.).
Roller pump
The pump console usually comprises several rotating motor-driven pumps that peristaltically "massage" tubing. This action gently propels the blood through the tubing. This is commonly referred to as a roller pump, orperistaltic pump
A peristaltic pump, also commonly known as a roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained in a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. Most peristaltic pumps work t ...
. The pumps are more affordable than their centrifugal counterparts, but are susceptible to overpressurization if the lines become clamped or kinked. They are also more likely to cause a massive air embolism and require constant, close supervision by the perfusionist.
Oxygenator
Theoxygenator
An oxygenator is a medical device that is capable of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood of human patient during surgical procedures that may necessitate the interruption or cessation of blood flow in the body, a critical organ or ...
is designed to add oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as wel ...
to infused blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the c ...
and remove some of the carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
from the venous blood
Venous blood is deoxygenated blood which travels from the peripheral blood vessels, through the venous system into the right atrium of the heart. Deoxygenated blood is then pumped by the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary artery whic ...
. Cardiac surgery was made possible by CPB using bubble oxygenator A bubble oxygenator is an early implementation of the oxygenator used for cardiopulmonary bypass. It has since been supplanted by the membrane oxygenator
as a result of advances in material science. Some continue to promote it as a low-cost altern ...
s, but membrane oxygenator
A membrane oxygenator is a device used to add oxygen to, and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. It can be used in two principal modes: to imitate the function of the lungs in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), and to oxygenate blood in longer term ...
s have supplanted bubble oxygenators since the 1980s. The main reasons for this are that membrane oxygenator
A membrane oxygenator is a device used to add oxygen to, and remove carbon dioxide from the blood. It can be used in two principal modes: to imitate the function of the lungs in cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), and to oxygenate blood in longer term ...
s tend to generate many fewer micro-bubbles, referred to as gaseous microemboli, which is generally considered harmful to the patient and reduce damage to blood cells, compared to bubble oxygenator A bubble oxygenator is an early implementation of the oxygenator used for cardiopulmonary bypass. It has since been supplanted by the membrane oxygenator
as a result of advances in material science. Some continue to promote it as a low-cost altern ...
s. More recently, the use of hollow-fiber oxygenators has become more widespread. These derivatives of membrane oxygenators further reduce the occurrence of microemboli by reducing the direct air-blood interface while simultaneously providing adequate gas exchange.
Another type of oxygenator gaining favour recently is the heparin-coated blood oxygenator which is believed to produce less systemic inflammation and decrease the propensity for blood to clot in the CPB circuit.
Heat exchangers
Because hypothermia is frequently used in CPB to reduce metabolic demands (including that of the heart), heat exchangers are implemented to warm and cool blood within the circuit. The heating and cooling is accomplished by passing the line through a warm or ice water bath. A separate heat exchanger is required for the cardiopledgia line.Cannulae
Multiplecannula
A cannula (; Latin meaning 'little reed'; plural or ) is a tube that can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid or for the gathering of samples. In simple terms, a cannula can surround the inner or outer surfaces ...
e are sewn into the patient's body in a variety of locations, depending on the type of surgery. A venous cannula removes oxygen depleted venous blood from a patient's body. An arterial cannula infuses oxygen-rich blood into the arterial system. The main determinants of cannula size selection is determined by the patient's size and weight, anticipated flow rate, and the size of the vessel being cannulated. A cardioplegia
Cardioplegia is intentional and temporary cessation of cardiac activity, primarily for cardiac surgery.
Overview
The word ''cardioplegia'' combines the Greek ''cardio'' meaning the "heart", and ''plegia'' "paralysis". Technically, this means a ...
cannula delivers a cardioplegia solution to cause the heart to stop beating.
Some commonly used cannulation sites:
Cardioplegia
Cardiopledgia is a fluid solution used to protect the heart during CPB. It is delivered via a cannula to the opening of the coronary arteries (usually by way of the aortic root) and/or to the cardiac veins (by way of the coronary sinus). These delivery methods are referred to antegrade and retrograde, respectively. Cardiopledgia solution protects the heart by arresting (i.e. stopping) the heart, thereby decreasing its metabolic demand. There are multiple types of cardiopledgia solutions, but most work by inhibiting fast sodium currents in the heart, thereby preventing conduction of theaction potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, ...
. Other types of solutions act by inhibiting calcium's actions on myocyte
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscl ...
s.
Technique
Pre-operative planning
CPB requires significant forethought before surgery. In particular, the cannulation, cooling, and cardio-protective strategies must be coordinated between thesurgeon
In modern medicine, a surgeon is a medical professional who performs surgery. Although there are different traditions in different times and places, a modern surgeon usually is also a licensed physician or received the same medical training as ...
, anesthesiologist
Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, ...
, perfusionist
A cardiovascular perfusionist, clinical perfusionist or perfusiologist, and occasionally a cardiopulmonary bypass doctor or clinical perfusion scientist, is a healthcare professional who operates the cardiopulmonary bypass machine (heart–lung ma ...
, and nursing staff.
Cannulation strategy
The cannulation strategy varies on several operation-specific and patient-specific details. The typical arterial cannulation involves the placement of a single cannulation within distalascending aorta
The ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of the third costal cartilage behind the left half of the sternum.
Structure
It passes obliqu ...
. The most simple form on involves placement of a single cannula (known as a dual-stage cannula) passed through the right atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
and into the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
. In some operations, such as those involving the tricuspid
The tricuspid valve, or right atrioventricular valve, is on the right dorsal side of the mammalian heart, at the superior portion of the right ventricle. The function of the valve is to allow blood to flow from the right atrium to the right ven ...
or mitral valve
The mitral valve (), also known as the bicuspid valve or left atrioventricular valve, is one of the four heart valves. It has two cusps or flaps and lies between the left atrium and the left ventricle of the heart. The heart valves are all one-w ...
, two cannula are used—one is passed through the inferior vena cava and one through the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein th ...
. This is known as bi-caval cannulation.
Intra-operative technique
A CPB circuit must be primed with fluid and all air expunged from the arterial line/cannula before connection to the patient. The circuit is primed with a crystalloid solution and sometimes blood products are also added. Prior to cannulation (typically after opening the pericardium when using central cannulation),heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
or another anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
is administered until the activated clotting time
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an interv ...
is above 480 seconds.
The arterial cannulation site is inspected for calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature Mat ...
or other disease. Preoperative imaging or an ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequency, frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing range, hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hea ...
probe may be used to help identify aortic calcifications that could potentially become dislodged and cause an occlusion or stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
. Once the cannulation site has been deemed safe, two concentric, diamond-shaped pursestring sutures are placed in the distal ascending aorta. A stab incision with a scalpel
A scalpel, lancet, or bistoury is a small and extremely sharp bladed instrument used for surgery, anatomical dissection, podiatry and various arts and crafts (either called a hobby knife or an X-acto knife.). Scalpels may be single-use disposa ...
is made within the pursestrings and the arterial cannula is passed through the incision. It is important the cannula is passed perpendicular to the aorta to avoid creating an aortic dissection
Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of severe chest or ...
. The pursestrings sutures are cinched around the cannula using a tourniquet and secured to the cannula. At this point, the perfusionist advances the arterial line of the CPB circuit and the surgeon connects the arterial line coming from the patient to the arterial line coming from the CPB machine. Care must be taken to ensure no air is in the circuit when the two are connected, or else the patient could develop an air embolism
An air embolism, also known as a gas embolism, is a blood vessel blockage caused by one or more bubbles of air or other gas in the circulatory system. Air can be introduced into the circulation during surgical procedures, lung over-expansion i ...
. Other sites for arterial cannulation include the axillary artery
In human anatomy, the axillary artery is a large blood vessel that conveys oxygenated blood to the lateral aspect of the thorax, the axilla (armpit) and the upper limb. Its origin is at the lateral margin of the first rib, before which it is ...
, brachiocephalic artery
The brachiocephalic artery (or brachiocephalic trunk or innominate artery) is an artery of the mediastinum that supplies blood to the right arm and the head and neck.
It is the first branch of the aortic arch. Soon after it emerges, the brachiocep ...
, or femoral artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the fem ...
.
Aside from the differences in location, venous
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated b ...
cannulation is performed similarly to arterial cannulation. Since calcification of the venous system
Veins are blood vessels in humans and most other animals that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated b ...
is less common, the inspection or use of an ultrasound for calcification at the cannulation sites is unnecessary. Also, because the venous system is under much less pressure than the arterial system, only a single suture is required to hold the cannula in place. If only a single cannula is to be used (dual-stage cannulation), it is passed through the right atrial appendage
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two atr ...
, through the tricuspid valve, and into the inferior vena cava. If two cannula are required (single-stage cannulation), the first one is typically passed through the superior vena cava and the second through the inferior vena cava. The femoral vein
In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) as the continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at th ...
may also be cannulated in select patients.
If the heart must be stopped for the operation, cardioplegia
Cardioplegia is intentional and temporary cessation of cardiac activity, primarily for cardiac surgery.
Overview
The word ''cardioplegia'' combines the Greek ''cardio'' meaning the "heart", and ''plegia'' "paralysis". Technically, this means a ...
cannulas are also required. Antegrade cardiopledgia (forward flowing, through the heart's arteries), retrograde cardiopledgia (backwards flowing, through the heart's veins), or both types may be used depending on the operation and surgeon preference. For antegrade cardiopledgia, a small incision is made in the aorta proximal to the arterial cannulation site (between the heart and arterial cannulation site) and the cannula is placed through this to deliver cardiopledgia to the coronary arteries
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ of ...
. For retrograde cardiopledgia, an incision is made on the posterior (back) surface of the heart through the right ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper ...
. The cannula is placed in this incision, passed through the tricuspid valve, and into the coronary sinus
In anatomy, the coronary sinus () is a collection of veins joined together to form a large vessel that collects blood from the heart muscle ( myocardium). It delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium, as do the superior and inferior ven ...
. The cardiopledgia lines are connected to the CPB machine.
At this point, the patient is ready to go on bypass. Blood from the venous cannula(s) enters the CPB machine by gravity where it is oxygenated and cooled (if necessary) before returning to the body through the arterial cannula. Cardiopledgia can now be administered to stop the heart, and a cross-clamp is placed across the aorta between the arterial cannula and cardiopledgia cannula to prevent the arterial blood from flowing backwards into the heart.
Once the patient is ready to come off of bypass support, the cross-clamp and cannulas are removed and protamine sulfate
Protamine sulfate is a medication that is used to reverse the effects of heparin. It is specifically used in heparin overdose, in low molecular weight heparin overdose, and to reverse the effects of heparin during delivery and heart surgery. ...
is administered to reverse the anticoagulative effects of heparin.
History
 The Austrian-German physiologist Maximilian von Frey constructed an early prototype of a heart-lung machine in 1885 at
The Austrian-German physiologist Maximilian von Frey constructed an early prototype of a heart-lung machine in 1885 at Carl Ludwig
Carl Friedrich Wilhelm Ludwig (; 29 December 1816 – 23 April 1895) was a German physician and physiologist. His work as both a researcher and teacher had a major influence on the understanding, methods and apparatus used in almost all branches ...
's Physiological Institute of the University of Leipzig
Leipzig University (german: Universität Leipzig), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 Decemb ...
.
However, such machines were not feasible before the discovery of heparin
Heparin, also known as unfractionated heparin (UFH), is a medication and naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan. Since heparins depend on the activity of antithrombin, they are considered anticoagulants. Specifically it is also used in the treatm ...
in 1916, which prevents blood coagulation
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
. The Soviet scientist Sergei Brukhonenko
Sergei Sergeevich Brukhonenko (russian: Серге́й Серге́евич Брюхоненко; 30 April 1890 – 20 April 1960) was a Soviet physician, biomedical scientist and technologist during the Stalinist era. Brukhonenko's research was ...
developed a heart-lung machine for total body perfusion in 1926 named the ''Autojektor'', which was used in experiments with canines. A team of scientists at the University of Birmingham
, mottoeng = Through efforts to heights
, established = 1825 – Birmingham School of Medicine and Surgery1836 – Birmingham Royal School of Medicine and Surgery1843 – Queen's College1875 – Mason Science College1898 – Mason Univers ...
(including Eric Charles, a chemical engineer) were among the pioneers of this technology.
Dr. Clarence Dennis
Clarence Dennis (June 16, 1909 – July 11, 2005) was an American cardiothoracic surgeon best known for his work in pioneering cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). He had invented one of the first heart-lung bypass machines, and in 1951 he became the f ...
led the team at the University of Minnesota Medical Center that on April 5, 1951, conducted the first human operation involving open cardiotomy with temporary mechanical takeover of both heart and lung functions. The patient did not survive due to an unexpected complex congenital heart defect. One member of the team was Dr. Russell M. Nelson
Russell Marion Nelson Sr. (born September 9, 1924) is an American religious leader and retired surgeon who is the 17th and current president of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS Church). Nelson was a member of the LDS Church ...
, who later became president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
and who performed the first open heart surgery in Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
.
The first successful mechanical support of left ventricular function was performed on July 3, 1952, by Forest Dewey Dodrill
Forest Dewey Dodrill (January 26, 1902 – June 28, 1997) was a medical doctor at Harper University Hospital at Wayne State University in Michigan who performed the first successful open heart surgery using a mechanical pump.
Biography
Dodrill wa ...
using a machine co-developed with General Motors, the Dodrill-GMR. The machine was later used to support right ventricular function.
The first successful open heart procedure on a human utilizing the heart lung machine was performed by John Gibbon
John Gibbon (April 20, 1827 – February 6, 1896) was a career United States Army officer who fought in the American Civil War and the Indian Wars.
Early life
Gibbon was born in the Holmesburg section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the fourt ...
and Frank F. Allbritten, Jr. on May 6, 1953, at Thomas Jefferson University Hospital
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital is the flagship hospital of Jefferson Health, a multi-state non-profit health system based in Philadelphia. The hospital serves as the teaching hospital for Thomas Jefferson University.
History
Originally form ...
in Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
. They repaired an atrial septal defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this d ...
in an 18-year-old woman. Gibbon's machine was further developed into a reliable instrument by a surgical team led by John W. Kirklin
John Webster Kirklin (April 5, 1917 – April 21, 2004) was an American cardiothoracic surgeon, general surgeon, prolific author and medical educator who is best remembered for refining John Heysham Gibbon, John Gibbon's cardiopulmonary bypass, h ...
at the Mayo Clinic
The Mayo Clinic () is a nonprofit American academic medical center focused on integrated health care, education, and research. It employs over 4,500 physicians and scientists, along with another 58,400 administrative and allied health staff, ...
in Rochester, Minnesota
Rochester is a city in the U.S. state of Minnesota and the county seat of Olmsted County. Located on rolling bluffs on the Zumbro River's south fork in Southeast Minnesota, the city is the home and birthplace of the renowned Mayo Clinic.
Acco ...
in the mid-1950s.
 The oxygenator was first conceptualized in the 17th century by
The oxygenator was first conceptualized in the 17th century by Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
and developed into practical extracorporeal oxygenators by French and German experimental physiologists in the 19th century. Bubble oxygenators have no intervening barrier between blood and oxygen, these are called 'direct contact' oxygenators. Membrane oxygenators introduce a gas-permeable membrane between blood and oxygen that decreases the blood trauma of direct-contact oxygenators. Much work since the 1960s focused on overcoming the gas exchange handicap of the membrane barrier, leading to the development of high-performance microporous hollow-fibre oxygenators that eventually replaced direct-contact oxygenators in cardiac theatres. In 1983, Ken Litzie patented a closed emergency heart bypass system which reduced circuit and component complexity. This device improved patient survival after cardiac arrest because it could be rapidly deployed in non-surgical settings.
In 1983, Ken Litzie patented a closed emergency heart bypass system which reduced circuit and component complexity. This device improved patient survival after cardiac arrest because it could be rapidly deployed in non-surgical settings.
References
External links
International Consortium For Evidence-Based Perfusion
*
Multimedia Manual of Cardiothoracic Surgery. Cardiopulmonary bypass collection.
Selected papers of Clarence Dennis, credited with the first attempt at cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. {{Authority control Medical equipment American inventions German inventions Soviet inventions